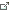
The effect of continental drift on plants and animals.
- Future
- Poor. This plant group would die out at the end of the Permian.
- Favoritefood
- -
- Favorite place
- Wetlands
- Founding place
- Arroio dos Chachorros, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil
Glossopteris indica
Large wetland forests grew in the Southern Hemisphere during the Permian. They were dominated by Glossopteris, a group of seed-bearing trees that shed their leaves in the autumn. The leaves accumulated and gradually became vast deposits of coal.
The climate changed drastically toward the end of the Permian and several large plant groups became extinct, including Glossopteris.
- Future
- Poor. This plant group would die out at the end of the Permian.
- Favoritefood
- -
- Favorite place
- Wetlands
- Founding place
- Vereeniging, Gauteng, South Africa
Glossopteris
Large wetland forests grew in the Southern Hemisphere during the Permian. They were dominated by Glossopteris, a group of seed-bearing trees that shed their leaves in the autumn. The leaves accumulated and gradually became vast deposits of coal.
The climate changed drastically toward the end of the Permian and several large plant groups became extinct, including Glossopteris.
- Future
- Poor. This type of reptile would die out at the end of the Permian.
- Favoritefood
- Crustaceans
- Favorite place
- Lakes and rivers
- Founding place
- Irati, Brasil
Mesosaurus
Mesosaurus was one of the first reptiles that spent its entire life in water. It was adapted for such a life, with a long body, very strong ribs, large and probably webbed feet, and a powerful long tail. It fed on crustaceans and other water-dwelling arthropods. Mesosaurus gave birth to live offspring.
Fossils of Mesosaurus have been found in both southern Africa and eastern South America, providing good evidence for the theory of continental drift.
- Future
- Poor. This plant group would die out at the end of the Permian.
- Favoritefood
- -
- Favorite place
- Wetlands
- Founding place
- Egara, Bhurdwan, West Bengal, India
Glossopteris
Large wetland forests grew in the Southern Hemisphere during the Permian. They were dominated by Glossopteris, a group of seed-bearing trees that shed their leaves in the autumn. The leaves accumulated and gradually became vast deposits of coal.
The climate changed drastically toward the end of the Permian and several large plant groups became extinct, including Glossopteris.
- Future
- Good. These reptiles would go extinct in the Triassic, but they belong to the group that gave rise to mammals.
- Favoritefood
- Plants
- Favorite place
- Plains
- Founding place
- Murraysburg, South Africa
Dicynodont
Dicynodonts were mammal-like reptiles with three distinctive features: two small tusks but no other teeth; the lower jaw consisted of several bones; and the skull had a ”third eye”. Their arms and the short, broad hands were ideal for digging with.
Small dicynodonts were often preserved as complete skeletons because they died in their burrows, which protected the corpses from scavengers, for example.